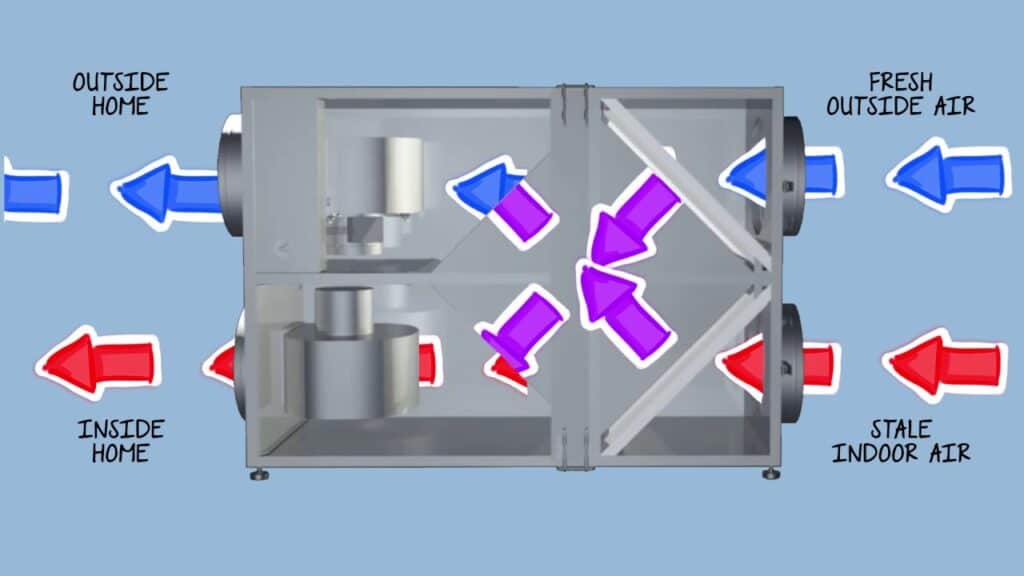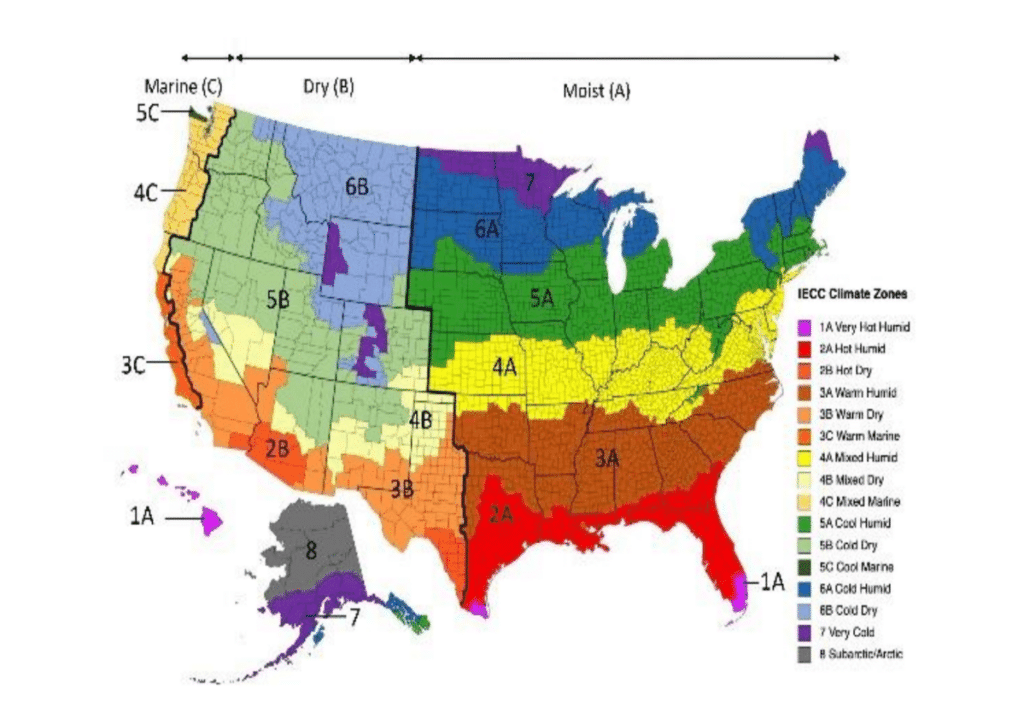
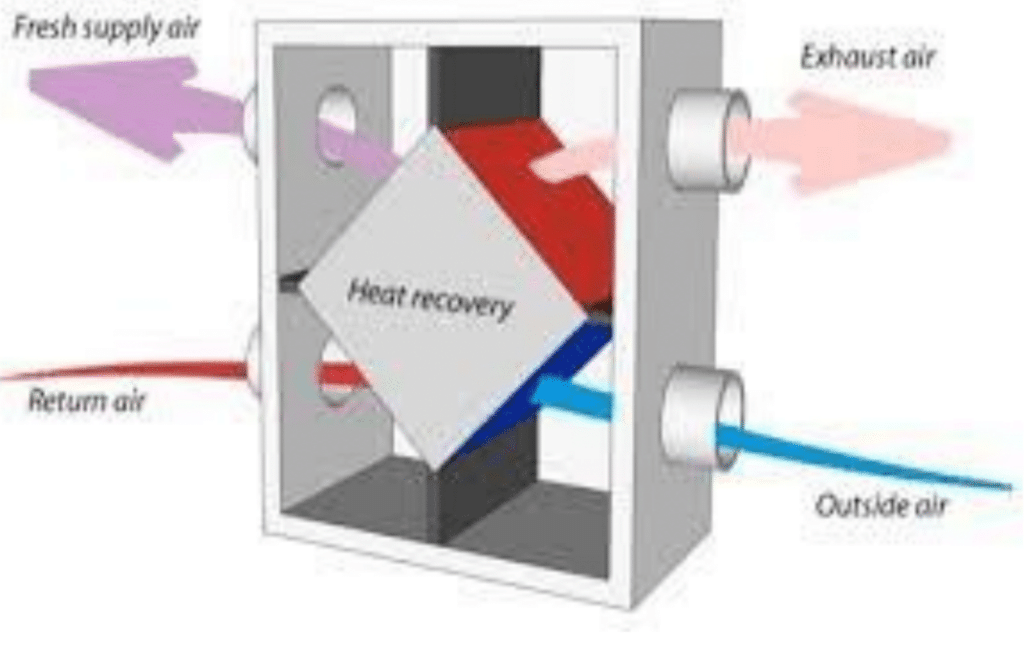
Conversely, in southern states characterized by high outdoor humidity and temperature, relying solely on ventilation to control indoor humidity is often ineffective. Introducing moist, warm air from outside can exacerbate humidity issues rather than alleviate them. In these regions, a more effective strategy involves using Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs), Dehumidifiers, and Properly Sized HVAC systems.